A complete guide by ArmorGuard for procurement officers, tactical brands, and law enforcement agencies.
What Are NIJ Ballistic Levels?
NIJ ballistic levels define the resistance capability of body armor against specific ammunition types. Each level—IIA, II, IIIA, III, and IV—represents a progressive increase in protection, standardized under the NIJ 0101.06 and upcoming NIJ 0101.07 protocols.
These classifications ensure consistent performance benchmarks for military, law enforcement, and security applications, guiding the selection and testing of ballistic materials worldwide.
ArmorGuard manufactures ballistic protection products in alignment with NIJ methodologies and customer-defined requirements. As a custom defense manufacturer, ArmorGuard conducts on-demand ballistic testing through accredited third-party laboratories to validate performance under the specific NIJ level requested by each client.
How NIJ Testing Defines Protection Levels
NIJ testing replicates real-world ballistic threats to evaluate the protection capability of armor systems.
Certified laboratories conduct controlled firings using standard ammunition types at defined velocities, measuring both penetration and back-face deformation (BFD) to assess energy absorption and structural integrity.
This process ensures that armor performance remains consistent, repeatable, and comparable across different environments and threat profiles—critical for defense, police, and tactical applications.
ArmorGuard follows NIJ and STANAG test methodologies during prototype evaluation and production verification, with ballistic testing conducted on demand at accredited laboratories in accordance with client specifications.
NIJ Ballistic Level Chart (IIA–IV)
The table below summarizes each NIJ level, ammunition type, and typical use case:
| Test Parameter | Description | Typical NIJ Reference |
| Ammunition Type | 9mm FMJ, .44 Magnum, 7.62x51mm NATO, etc. | Per NIJ 0101.06 / 0101.07 |
| Velocity (m/s) | Standard impact speed for each level | Defined by the NIJ standard tables |
| Back-Face Deformation (BFD) | Max. 44 mm (NIJ limit) | Measured with Roma clay backing |
| V50 Ballistic Limit | The velocity at which 50% of the projectiles penetrate | Per STANAG 2920 methodology |
| Test Distance | Typically 5–15 m, depending on ammunition | NIJ and client-specific protocols |
| Shot Placement | Multi-hit pattern testing | Defined by level and plate geometry |
How to Choose the Right NIJ Level
Selecting the appropriate NIJ protection level depends on operational requirements, threat environment, and end-user comfort.
Procurement teams are advised to align armor performance with mission needs—not simply opt for the heaviest rating. Over-specifying armor can reduce mobility and operational endurance without added tactical benefit.
For structured decision-making, refer to the Body Armor Procurement Guide or consult ArmorGuard engineers for customized recommendations.
General recommendations:
| NIJ Level | Protection Scope | Typical Applications |
| Level IIA – II | Handgun threats (9mm, .357 Magnum) | Concealed wear, low-threat urban patrols, private security |
| Level IIIA | High-velocity handgun rounds (.44 Magnum) | Standard police duty, VIP protection, special response units |
| Level III | Rifle rounds (7.62×51mm NATO, .308 Win) | Military patrols, border security, open-field operations |
| Level IV | Armor-piercing rifle threats | Combat missions, counter-terror units, high-risk defense operations |
Applications by User Group
Different organizations require tailored ballistic protection based on their mission profiles and operational environments. The table below summarizes typical armor deployment by user category.
| User Type | Recommended NIJ Level | Notes |
| Police Patrol Units | IIIA | Lightweight soft armor designed for handgun threats and daily duty comfort. |
| Military Infantry | III / IV | Rigid armor plates engineered to counter rifle fire and high-impact projectiles. |
| Security Guards | II / IIIA | Comfort-optimized soft vests for extended wear in urban and commercial environments. |
| VIP Protection / Close Protection | IIIA | Flexible covert vests for discreet protection under formal or civilian clothing. |
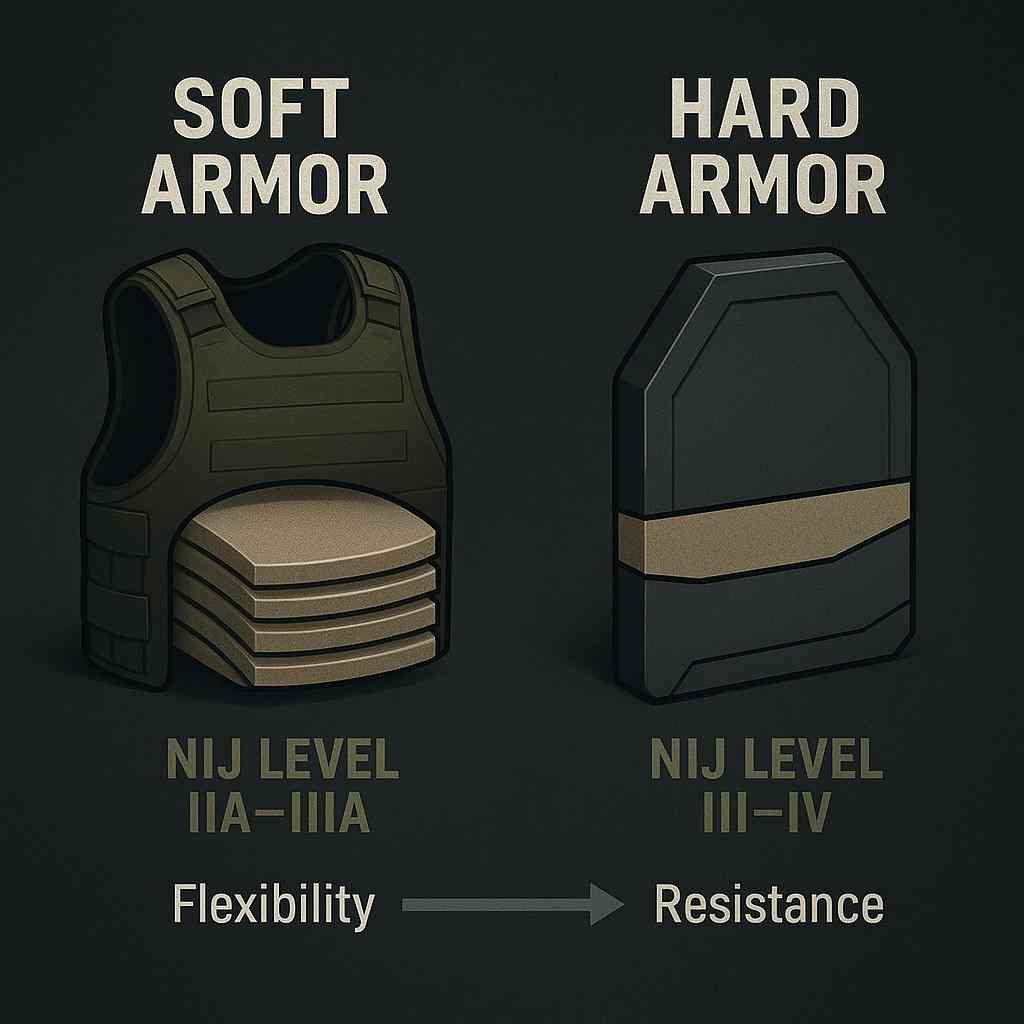
Soft vs Hard Armor Across NIJ Levels
Soft armor and hard armor serve distinct ballistic protection purposes within the NIJ framework.
- Soft Armor (NIJ Levels IIA – IIIA):
Constructed primarily from Aramid fibers (e.g., Kevlar®) or UHMWPE (e.g., Dyneema®).
Designed for handgun and submachine gun threats, soft armor offers flexibility, comfort, and concealability, making it suitable for law enforcement, VIP, and security use. - Hard Armor (NIJ Levels III – IV):
Utilizes ceramic strike faces, composite backings, or metal-reinforced structures.
Built to defeat rifle and armor-piercing rounds, hard armor prioritizes impact resistance and multi-hit performance for military and tactical applications.
| Parameter | Soft Armor (NIJ IIA–IIIA) | Hard Armor (NIJ III–IV) | Notes |
| Material Composition | Aramid / UHMWPE | Ceramic + Composite Backing | Typical configurations |
| Areal Density (kg/m²) | 3.5 – 5.0 | 18 – 28 | Average for the protection level |
| Panel Weight (per m²) | 3 – 5 kg | 20 – 30 kg | Depends on size and level |
| Thickness (mm) | 6 – 10 | 18 – 25 | Varies by threat level |
| Threat Resistance | Handgun rounds | Rifle / AP rifle rounds | NIJ specified |
| Typical Users | Police, VIP, Security | Military, Tactical Units | Application categories |
Key Takeaways for Procurement Teams
When selecting ballistic protection, procurement officers should ensure technical accuracy, documentation transparency, and ergonomic suitability. Proper evaluation prevents mismatches between operational needs and the protection provided.
Procurement Best Practices
- Match NIJ Level with Actual Threats: Choose armor based on verified ballistic threat levels—not solely on budget or perception.
- Request NIJ Test Documentation: Always ask for official NIJ or STANAG ballistic test reports from accredited laboratories.
- Verify Labeling and Traceability: Check that each product includes a serial number, a lot identifier, and a batch test reference.
- Prioritize Comfort and Ergonomics: Select designs optimized for long-duration missions and mobility under load.
- Engage Reliable OEM/ODM Partners: For customized ballistic sourcing, ArmorGuard provides on-demand testing, labeling, and documentation for OEM and ODM manufacturing.
| Inspection / Acceptance Item | Requirement | Provided by ArmorGuard |
| Ballistic Certification Report | NIJ / STANAG / VPAM test report | Available upon the client’s testing project |
| Material Certificates | Aramid, UHMWPE, and Ceramic composition reports | Included in QA package |
| Serial Number Record | Product ID + batch test correlation | Embedded in the label and QA file |
| Visual / Dimensional Inspection | Check stitching, labeling, and plate alignment | Conducted pre-shipment |
| Factory QA Plan | Quality assurance workflow document | Available upon request |
| Third-Party Verification | Independent ballistic test result | Arranged upon client demand |
ArmorGuard integrates R&D, ballistic production, and quality assurance into a single manufacturing framework.
- Production Base: Thailand (dedicated ballistic workshop)
- Core Expertise: Aramid, UHMWPE, Ceramic Composite Systems
- Testing Collaboration: Accredited laboratories in Asia & Europe
- OEM / ODM Services: For tactical brands, defense contractors, and police suppliers
Every ArmorGuard product can be validated through on-demand NIJ or STANAG testing based on client requirements, ensuring compliance, traceability, and performance confidence.



