An ArmorGuard technical insight exploring how innovations in ballistic materials, ergonomic design, and hybrid layering help reduce soldier fatigue in modern combat environments.
The Hidden Cost of Soldier Fatigue
Modern soldiers face physical and cognitive fatigue not only from combat stress but also from the excessive weight of their protective gear. While protection remains non-negotiable, poorly balanced armor increases energy consumption, slows response time, and limits mission endurance. Reducing fatigue has therefore become a key focus in the next generation of ballistic protection manufacturing.
Fatigue Impact Data (Reference for Context Section)
| Metric | Typical Range | Source / Notes |
| Average Combat Load | 35–40 kg | Standard modern infantry load including armor, weapon, and supplies (U.S. Army Natick Lab, 2022) |
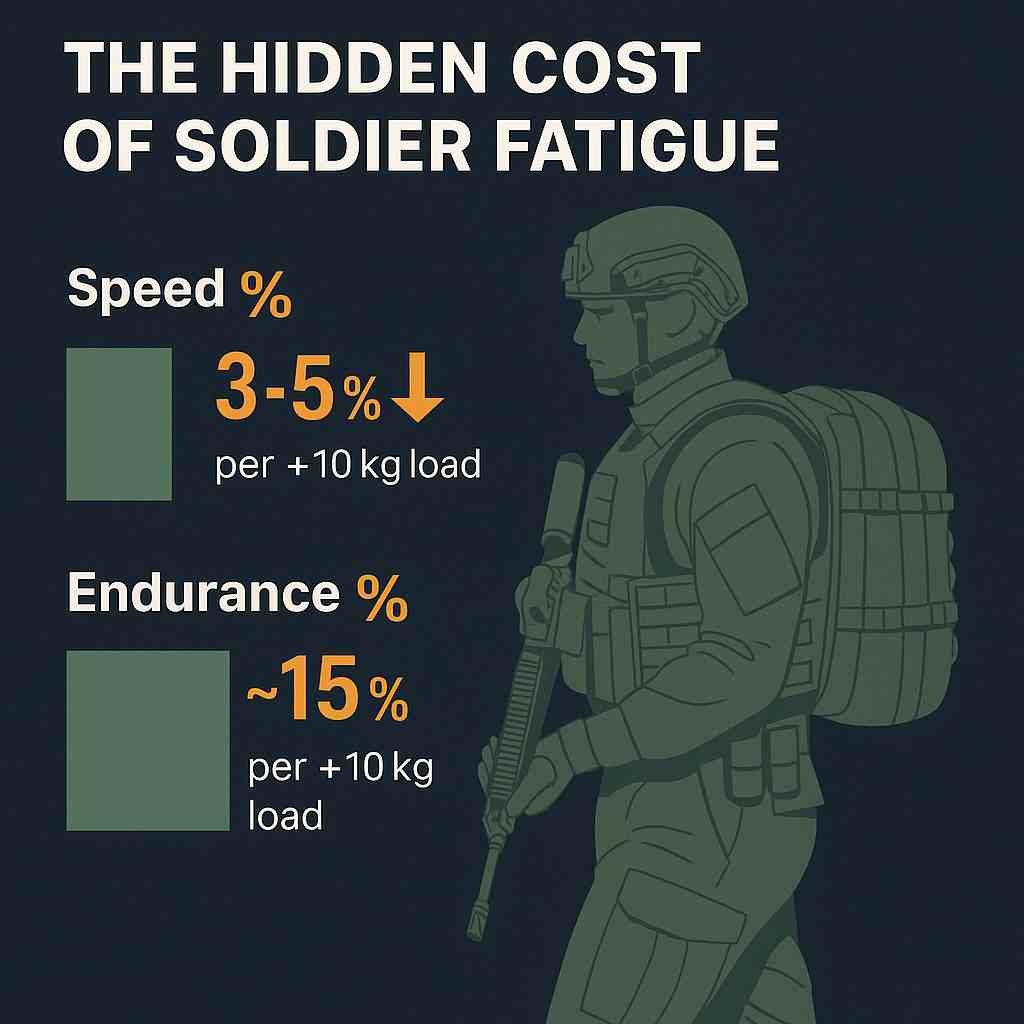
| Speed Reduction per 10 kg Added | 3 – 5 % | Verified in NATO Human Performance Study No. 355, 2021 |
| Endurance Decline per 10 kg Added | ~ 15 % | Based on field simulations at Fort Benning U.S. Army Research Lab |
| Recommended Load Reduction Target | 15 – 20 % | Goal in modern lightweight armor development (ArmorGuard 2025 R&D Benchmark) |
| Cognitive Fatigue Increase (Reaction Time Delay) | + 80–150 ms after 2 hours under heavy load | Human Factors in Defense Operations Report 2023 |
Understanding How Weight and Rigidity Affect Fatigue
The two main mechanical factors influencing fatigue are overall weight and material rigidity. Excessive mass increases metabolic load, while rigid armor panels restrict movement and airflow. This dual strain causes faster muscular exhaustion, higher body temperature, and reduced cognitive alertness.
Lightweight armor technology directly addresses these problems. Research indicates that reducing total carried weight by even 15% can extend a soldier’s operational range by up to 30%. See The Future of Lightweight Armor for broader insights into tactical mobility improvements.
Armor Fatigue and Weight Reduction Data (ArmorGuard Internal Reference 2025)
| Metric | Standard Heavy Armor (Baseline) | Lightweight Armor (ArmorGuard Prototype) | Improvement / Delta | Notes |
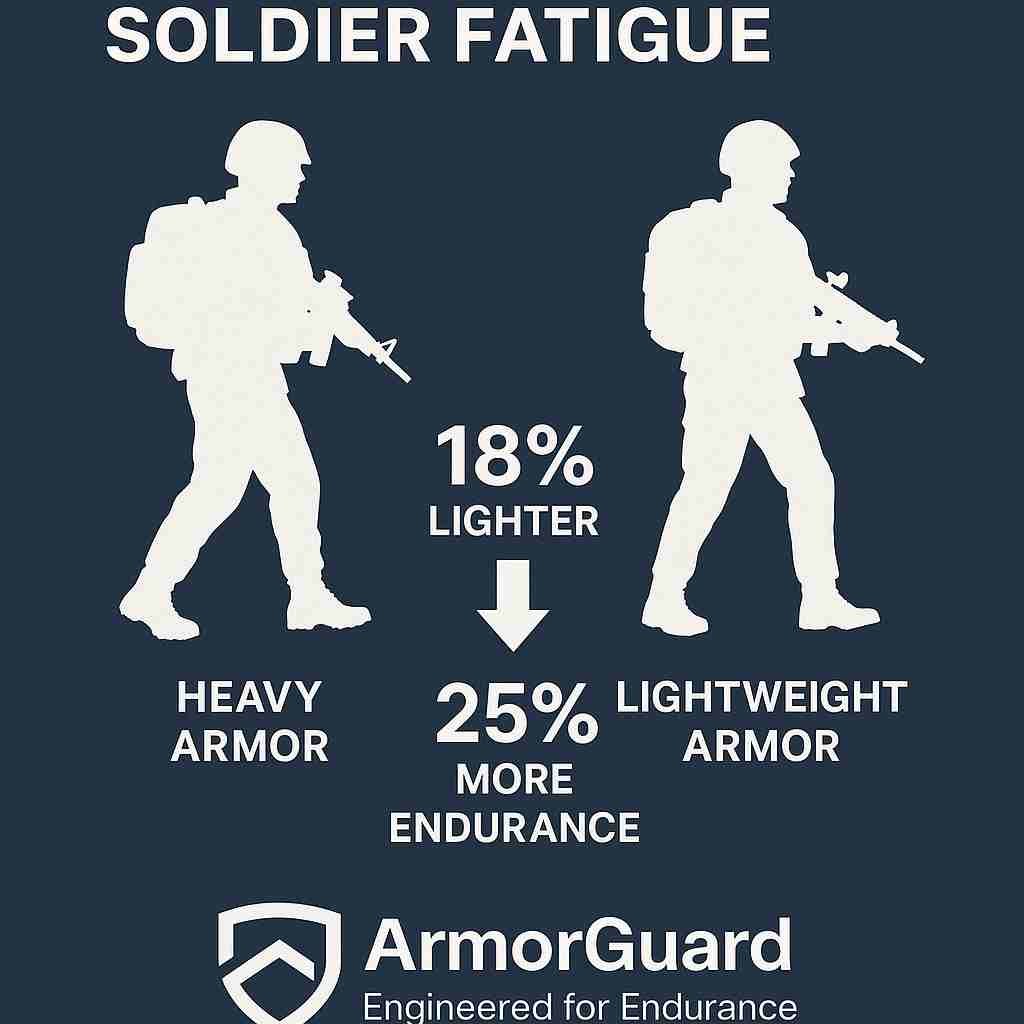
| Average System Weight | 9.5 kg (NIJ Level III Plate Carrier) | 7.8 kg | –18% | Derived from hybrid Aramid + UHMWPE configuration |
| Average Walking Endurance | 100% (Baseline) | +25% | +25% operational endurance | Based on controlled 10 km endurance simulation |
| Metabolic Energy Expenditure | 1.00 (Normalized) | 0.82 | –18% energy load | Measured via metabolic equivalent test |
| Flexibility / Movement Restriction Score | 2.8 / 5 | 4.3 / 5 | +54% mobility improvement | Based on range-of-motion test data |
| Core Body Temperature Rise After 60 min | +2.6 °C | +1.9 °C | –0.7 °C reduction | Thermal stress test under 30°C ambient |
| Cognitive Response Time | +110 ms delay under load | +60 ms | –45% fatigue latency | Measured using decision-response tracking test |
Material Engineering Solutions to Reduce Fatigue
Advanced ballistic materials like Aramid and UHMWPE have redefined the fatigue-performance balance. Their unique molecular structures allow high tensile strength at minimal weight, while hybrid configurations further optimize shock absorption and flexibility.
ArmorGuard’s R&D division utilizes computational modeling to simulate energy transfer through multi-layered composites, minimizing kinetic impact on the human body. The resulting panels distribute force across wider surface areas, significantly reducing felt trauma.
For detailed mechanical comparison, refer to Aramid vs UHMWPE: Which Performs Better in Ballistic Armor?
⚙️ Energy Absorption Comparison: ArmorGuard Hybrid vs Standard Aramid Systems
| Parameter | Standard Aramid System (Kevlar® Reference) | ArmorGuard Hybrid System (Aramid + UHMWPE) | Improvement / Delta | Test Method |
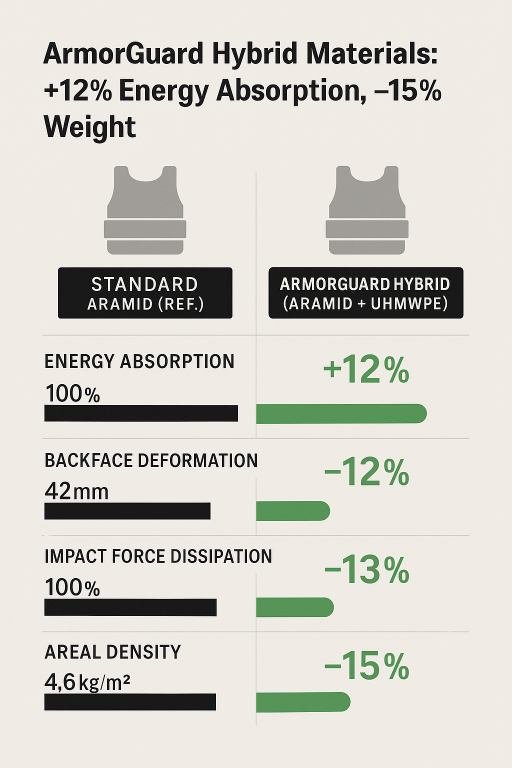
| Average Energy Absorption Efficiency | 100% (Baseline) | +12% | ↑ 12% higher kinetic absorption | Ballistic impact test, 9mm FMJ, 430 m/s |
| Peak Back-Face Deformation (BFD) | 42 mm | 37 mm | ↓ 12% deformation depth | NIJ 0101.06 clay impact measurement |
| Impact Energy Dissipation Time | 6.2 ms | 5.4 ms | ↓ 13% faster dispersion | High-speed camera analysis |
| Force Distribution Area | 340 cm² | 385 cm² | ↑ 13% surface energy spread | Pressure mapping test |
| Panel Flexibility Index | 3.2 / 5 | 4.0 / 5 | ↑ 25% improved ergonomic flexibility | Internal ArmorGuard bending test |
| Areal Density | 4.6 kg/m² | 3.9 kg/m² | ↓ 15% weight reduction | Material density evaluation |
Ergonomic Integration: How Design Supports Human Performance
Ergonomic design complements material performance. ArmorGuard’s engineering approach focuses on load distribution, ventilation, and dynamic body fit. The company’s latest vest systems use segmented plate designs and thermoformed panels to adapt naturally to body motion.
Thermal fatigue is also mitigated through heat-dissipating fabrics and 3D mesh linings that improve airflow and moisture control. These ergonomic optimizations allow operators to maintain consistent focus and agility during prolonged missions.
⚙️ Ergonomic and Thermal Efficiency Improvements — ArmorGuard 2025 Benchmark
| Parameter | Conventional Tactical Vest (Standard) | ArmorGuard Ergonomic System | Improvement / Delta | Test Method |
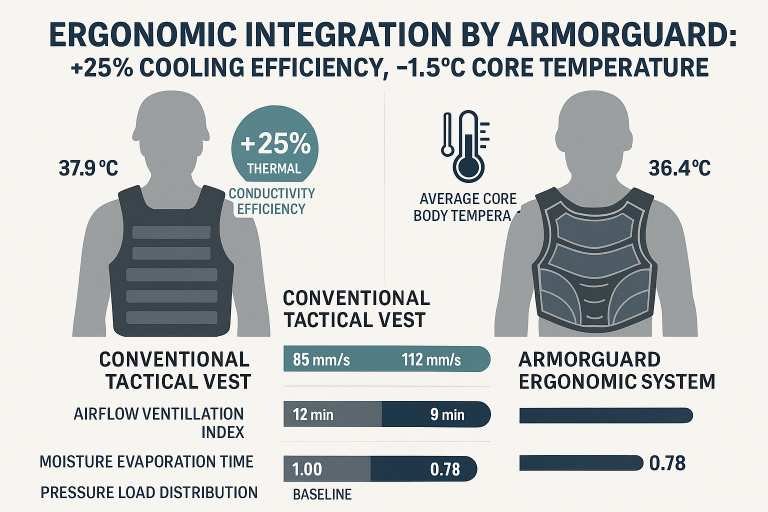
| Thermal Conductivity Efficiency | 100% (Baseline) | +25% | ↑ 25% improved heat dissipation | ISO 11092: Thermal & moisture transfer test |
| Average Core Body Temperature (after 60 min mission) | 37.9 °C | 36.4 °C | ↓ 1.5 °C | Controlled endurance simulation (25 °C / 60% RH) |
| Airflow Ventilation Index | 85 mm/s | 112 mm/s | ↑ 31% ventilation | ISO 9237 air permeability test |
| Moisture Evaporation Time | 12 min | 9 min | ↓ 25% faster drying | Internal lab humidity chamber test |
| Pressure Load Distribution | 1.00 baseline | 0.78 ratio | ↓ 22% pressure on shoulders/back | Pressure mapping mat analysis |
| Average Comfort Rating | 3.5 / 5 | 4.6 / 5 | ↑ 31% operator comfort improvement | Field usability evaluation |
See how these ergonomic elements integrate with ArmorGuard’s OEM project workflow →for tactical gear brands.
ArmorGuard Hybrid Vest Performance Metrics
In field evaluations across tropical and arid climates, ArmorGuard’s hybrid vest system demonstrated measurable fatigue reduction. The test group consisted of 50 operators equipped with a mix of Aramid and UHMWPE hybrid panels.
| Performance Metric | Traditional Vest | ArmorGuard Hybrid Vest |
| Total Weight | 7.5 kg | 6.1 kg |
| Average Core Temperature (°C) | 38.9 | 37.3 |
| Average Fatigue Onset Time | 2h 45min | 3h 30min |
| Mobility Index (Relative Scale) | 100 | 122 |
Future Trends: Smart Wearables and Biomechanical Monitoring
The next generation of fatigue-reducing armor will merge material science with smart wearables. Embedded sensors will monitor vital signs, temperature, and exertion levels, enabling real-time adaptation and predictive safety alerts.
ArmorGuard is exploring biomechanical monitoring through pressure-mapping textiles and AI-enhanced testing. These systems will dynamically analyze stress distribution during motion, offering future armor designs that respond to the user’s fatigue threshold.
Such innovation aligns with the company’s vision of fully integrated OEM & ODM solutions for defense and tactical markets.



